Do you know how to pop your ears? In this article, we are going to cover this topic. What is this and why is it necessary?
It is exasperating being ill with something such as chilly, influenza, or even a sinus disease that can make your ears feel like crap. The disagreeable ear strain which often comes with such disorders is the very last thing that you need when you are dealing with different symptoms such as a stuffy nose, continuous coughing, or even the overall malaise that accompanies being ill. Exactly why does your body haul your ears to the scenario when you are not feeling well?
These problems can influence the capability of your own ears to popup.
Table of Contents
1. Fluid in the ear
Fluid in the ear can prevent ears from popping up because the thickened fluid cubes the tube, that prevents fluid from draining to the rear of your throat. Sometimes this results from disease. Another reason for keeping fluid from the ear is a result of the enhancement of surrounding structures, like the adenoids or sinus tissue. If the sensory tube has been obstructed by surrounding tissue, then the removal of the tissue might also be required.
Fluid in the ear is normally treated by the surgical insertion of faux ear tubes, which enables the ear to drain and equalize pressure. You ought to be aware that in the event you have ear pads, you won’t have the ability to get your ears popup. This is due to the fact that the tube through your eardrum will automatically equalize pressure. Other titles for fluid from the ear contain serous otitis media, glue ear, and otitis media with effusion.
2. Excessive Candles Wax
Too much ear wax (cerumen) may also impair the purpose of your adrenal tube.
This does not mean that you should run out and get a ear candles or stick a cotton swab off your ear, since this will just push down the wax farther.
There are a couple ways your physician can remove the wax, and also it may be completed in their workplace. Wax may be removed with specific ear drops which encircle the wax, by irrigation, or using a special instrument known as a cerumen spoon, which the physician uses to”dig” out the wax.
3. Congestion:
Too much perspiration can liven up your tube and also make it hard to keep up the pressure from the middle ear area. Congestion-related to allergies could be aided by taking a decongestant medicine before getting in a plane or going on a road trip with altitude gain. A cold virus is also a frequent reason for congestion, however when it lasts more than about three weeks, then you might be coping with allergies or a different condition that needs to be assessed by a doctor.
4. Patulous Eustachian Tube:
The patulous eustachian tube is a really rare disorder where the adrenal tube fails to close and stays open all the time.
- Tinnitus
- Autophony (if your voice looks abnormally loud for you personally )
- Hearing your breathing.
Other Reasons
For A number of the different reasons you might experience eustachian tube malfunction include:
- Sinusitis
- Nasal polyps
- Enlarged turbinates
- Tonsillitis
Normally, an ENT is going to have the ability to help control symptoms from some of the above-mentioned difficulties with medications or surgery. But you need to plan ahead and have these problems resolved before traveling in the event that you would like to maximize your pleasure while minimizing any pain related to pressure fluctuations.
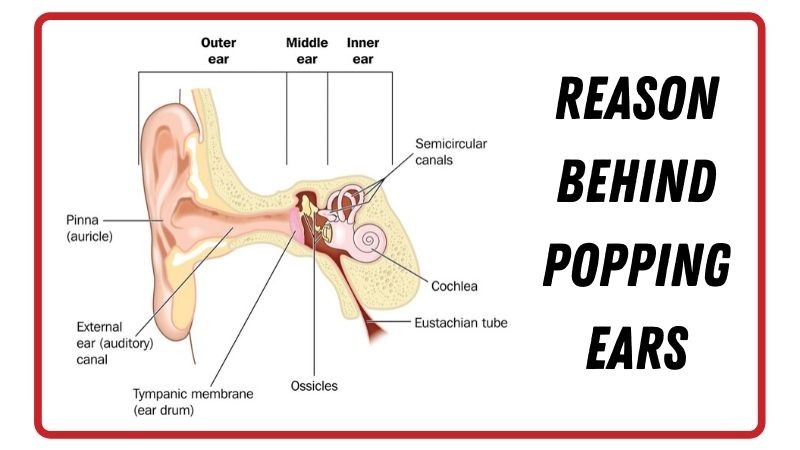
Why ear pressure occurs when you are ill?
It is typical for your own ears to feel nostalgic once you’ve got an illness or disease that affects the general area of your mind. Since our nose, ears, and throat are closely linked, an issue in 1 area often leads to another.
A lot of the purpose of the ear-nose-throat system hinges tiny canals known as the Eustachian tubes. Each ear has these narrow passageways to attach the center ear (the component containing the eardrum together with small bones which assist transport sound) into the rear of the nasal passages and upper neck. These tubes available and shut frequently to correct the air pressure in your middle ear, then eliminate natural fluids out of the middle ear, and circulate fresh air within your ear.
Should you are feeling tension, pain, or the feeling of your ears being plugged plus they won’t pop, you might have an inherent ear illness that’s affecting the role of your adrenal (eustachian) tube.
Way to relieve ear pressure when you are ill
Fortunately, ear stress generally goes off when the underlying disease or disease clears up. This can either occur naturally (in the event of something such as a cold) or via prescribed drugs (in the event of something such as a sinus infection).
Any health condition which affects your eustachian tube may alter your normal ability to equalize the pressure on your ears.
If the pressure gap continues to and you are not able to receive your ears or soda, you can experience ear discomfort and also receive a ruptured eardrum (also referred to as barotrauma).
Try these suggestions to help to equalize the pressure on your ears.
If you’re traveling with a baby or toddler you might not have the ability to make them perform some of the above mentioned. It’s possible to simulate exactly the very same activities by making them use a jar, suck on a pacifier, or provide them a beverage.
You may even try the very same tricks you may use whenever you are handling ear strain on a plane. These strategies are all made to open the Eustachian tubes, permitting airflow to equalize the strain on either side of your eardrums(how to pop your ears?):
- Swallowing
- Yawning
- Chew gum
- Suck on hard candy
- Use over-the-counter decongestants, like Afrin or Sudafed, before traveling
HOW TO TELL IF IT MORE
If your ear strain sticks around once you feel better (or for more than a week) and you also begin to experience difficulties like ear discomfort, fluid drainage, and hearing loss, you could be dealing with a ear infection. This sometimes happens whether the fluid that is built up on your inner ear gets infected with a bacteria or virus.
Should you guess that you may get an ear infection, certainly see a physician. Because of the marvels of modern medicine, they could have a thorough look inside your own ears and determine what’s behind your symptoms.
Your body naturally keeps a standard balance of air pressure on each side of your eardrum. After the pressure varies between the middle ear and the exterior, you may feel as though your ears are plugged. Based on the amount of stress change, you could even experience pain connected with the changes. Typically, as stress begins to develop, you can equalize the pressure on your ears .
However, as you ascend or descend quickly by flying, diving, or driving down and up a steep hill, the atmosphere in your middle ear area can at times have difficulty adjusting to the strain. This clicking or popping sensation happens as air moves in the top portion of the nose and throat via your eustachian tube in your middle ear.
Why Your Ears Won’t Pop in the Plane?
If your ears don’t pop and you are feeling as if they are obstructed or you’re having substantial ear pain, you must make an appointment with a physician. When you have symptoms of a ruptured eardrum, like blood or fluid draining from the ear, then an extreme earache accompanied by a soda and surprising pain, or difficulty hearing, then you need to visit a physician promptly.
If you are battling something such as an upper respiratory disease or Infection, your Eustachian tube openings can become partially blocked as a result of tissue inflammation and mucus secretions, and this redness has the potential to interfere with the normal operation of those tubes, possibly resulting in a pressure imbalance. This might give rise to a feeling of stuffiness. (It is like the plugged-up atmosphere you could get from the abrupt change in air pressure that occurs when you are in a plane.)
This inflammation may also lead to fluid buildup that contributes to ear strain. If the bronchial tubes are partially blocked, it is tougher for all those middle ear secretions to reduce the back of your neck (yum), which may result in an uncomfortably full feeling in the ear.
Should you really feel just like you always end up with ear pressure when you are ill, then know that a few people’s Eustachian tubes are obviously formed in a manner that makes them prone to ear distress whilst sick. Eustachian tubes that are thinner or more flat than ordinary make it easier for fluid to accumulate. (Children’s Eustachian tubes have been formed in this manner, which is part of the reason ear difficulties are somewhat more prevalent in children).
Other individuals may have more abundant mucous linings in the opening of the Eustachian tubes, which may make swelling more prone when they are ill.
How to pop your ears in a plane?
Popping the ears really helps you to open the eustachian tubes and then control the pressure in the ear.
Best Ways to Pop Your Ears:
1. Yawn or speak to open the mouth and trigger the Eustachian tube.
Yawning or even speaking may work well for moderate distress. A fake yawn, in which you just mimic the broad stretching of a the mouth, can do just fine.
Throughout at least one of these activities,”you are starting and closing that tube,” Quesnel states. “When you start and shut that tube you are equalizing pressure with the external world.”
Repeat every few seconds till you feel that your ears pop and there is relief in the strain.
2. Additionally, the gum movement may also help open the eustachian tubes.
Swallow fluid, or suck on candy to modify the pressure on your throat.
Swallowing helps to trigger the muscles which open the eustachian tube. Sipping water or sucking hard candies can help increase the requirement to consume. These approaches, advocated by physicians everywhere actually perform work.
If you are using the nasal spray, then give yourself a spray 30 minutes before takeoff, and at thirty minutes from descent.
These medications aren’t a cure-all, and it is still possible to have issues but you are able to maximize your ability to equalize stress by choosing a nasal spray.
3. Utilize a long-acting nasal decongestant.
Utilize a long-acting nasal decongestant to cancel any swelling which might be happening in your nose and interfering with your Eustachian tube. If you are using the nasal spray, then give yourself a spray 30 minutes before takeoff, and at half an hour from descent.
These medications aren’t a cure-all, and it is still possible to have issues but you are able to maximize your ability to alleviate stress by choosing a nasal spray.
4. Valsalva maneuver…
If yawning and swallowing don’t do the job, have a deep breath and then pinch the nose closed. Maintaining the mouth shut, attempt to blow air through the nose softly.
It’s ideal to be careful when doing this move since there’s a small danger of rupturing the eardrum.
Gently pinch your nose closed. Then, together with your lips still squeezed in, proceed to blow out air (along with your nose pinched shut). This technique will aim some strain that is in the rear of the nose especially.
5. Toynbee maneuver
This ear-popping procedure is simple but powerful. Gently pinch your nose closed while concurrently consuming.
6. Frenzel maneuver
To execute this move, then pinch the nose shut and apply the tongue to create a clicking or”K” sound.
7. Avoid sleeping during takeoff or descent.
Should you pass on the airplane before it takes off, or are still sleeping while it is in descent, you won’t be swallowing, chewinggum, yawning, or performing some of those other items which will assist your ears pop obviously –and that absence of discharge (and relief) can cause you to awaken having a painful earache. Avoid this all by staying alert and making certain that your ears have popped (particularly during descent, once the elevation change is more debilitating ).
8. Use particular earplugs to impede down the rapid change in strain.
You might even use earplugs to help alleviate pain.
9. Apply a heating pad or hot washcloth for your ear.
Another method for opening up your Eustachian tube is employing heat with a hot washcloth or a heating system. The warmth will help unclog the Eustachian tube, and also, subsequently, open and shut to discharge built-up pressure.
10. Get pressure equalization tubes planted.
Sure, implants can seem severe, but if you are afflicted with pressure-related ear pain throughout each flight’s takeoff and landing (if you’ve got a cold or not), then you may have Eustachian tube malfunction. If you have this illness and you are a frequent traveler, then think about asking about pressure equalization tubes implants within your ears.
It is a easy, ten-minute procedure which aids your ears drain fluid and also modulate pressure. The implants continue one or two decades, and the process is normally done in a physician’s office.
Pressure equalization tubes, nevertheless, are a last resort, since they may cause ear infections or perforated ear drums. If you believe you might suffer with Eustachian tube disorder, speak with your physician about the implants and also perform a cost/benefit analysis.
11. Attempt Special Apparatus
There are devices available that could help clear the ears. These are especially helpful for men and women that are unable to utilize or execute the aforementioned maneuvers safely or efficiently.
There are some Kinds of apparatus:
Particular earplugs: All these special earplugs promise to help to modulate the circulation of air in the surroundings to the ear. It isn’t clear if they are genuinely powerful, but they’re affordable and risk-free.
Otovent: Both the Otovent and comparable apparatus mimic the moves used at the Valsalva maneuver. Pinch the open nostril shut and blow the balloon up with the nozzle at the initial nostril. This apparatus can be particularly valuable in kids or other individuals that aren’t able to utilize the Valsalva properly. Simply insert the unit into a single nostril, shut the flip side, and push a button.
Most devices are available to purchase online to assist people pop their ears securely.
12. Medicine
Experienced travelers often have a decongestant whenever they fly. Both tablets and intranasal sprays may operate, however an older research discovered oral drugs to be effective.
Taking the medication 30 minutes prior to take-off or landing can help shrink the mucous membranes in the nose along with eustachian tubes, which makes it much easier to clean the ears.
It’s more possible for the ears to eventually become clogged at this time and rare swallowing during sleep might be inadequate to clean them.
Babies sometimes find it hard to clean their earsas they aren’t able to intentionally consume or pop their ears.
Feeding (either in the breast or using a jar ) or supplying a pacifier can help the infant suck and swallow to be able to clean their ears. This may indicate waking the baby during uterus to prevent later distress.

What happens when ear pops?
- The eustachian tube helps flush fluid in the ear and also regulates air pressure between the ears and nose.
- Swallowing opens the tube and enables a little air bubble to move in the nose and to the ear.
- Many men and women see a little click or popping sound in the ear once they consume; this is a result of the flow of air to the ear.
- This procedure can help to maintain air pressure on each side of the eardrum exactly the same.
- When the eustachian tube becomes blocked, or when the external pressure is different compared to the interior pressure, it may cause that uneasy feeling that the ears are complete.
- The most frequent cause of a blocked eustachian tube would be a stuffy nose, like in the head cold or sinus disease.
- After the nose is filled or obstructed, it may stop the eustachian tubes from draining or filling with air correctly.
- A buildup of earwax is also a frequent cause of an obstructed or blocked eustachian tube.
- If the eustachian tube is blocked, then it prevents the air bubble out of moving to the middle ear, finally developing a vacuum and yanking on the eardrum.
- This may be embarrassing and may cause different problems in the ear, for example, hearing loss and nausea.
- The strain of the atmosphere inside the ear is typically the same as the strain beyond the ear. But in lower or higher altitudes, like when flying an airplane or deep-sea diving, the air pressure isn’t the same.
- Consequently, the eustachian tube should open wider and much more often so as to keep and equalize the brand new air pressure.
- Many men and women notice their ears feel worse at a plane through take-off and landing once the plane is creating a fast ascent or descent.
Additionally, it may occur anytime you can find rapid altitude or pressure fluctuations.
When to meet a doctor?
A person with clogged ears ought to visit their physician if the ears don’t pop employing these approaches. Anyone experiencing persistent pain or distress in their ear must contact their physician earlier.
The physician may suggest drugs, like decongestants or steroids, to help alleviate the ear, or antibiotics when a individual has a ear infection.
In rare instances, surgery might have to assist open the eardrum, drain the fluid, and equalize pressure at the ear.
All images by Canva.
Also Read:

